Artificial Intelligence (AI) and computer vision are transforming the healthcare industry, particularly in medical diagnostics. With advancements in deep learning and neural networks, computer vision is now capable of analyzing medical images with unprecedented accuracy. From detecting tumors in radiology scans to diagnosing retinal diseases through ophthalmology imaging, AI-powered computer vision is making healthcare diagnosis faster, more precise, and more accessible. This blog explores how AI is revolutionizing medical imaging, its impact on different medical fields, and the challenges that come with this technological evolution.
The Evolution of Computer Vision in Healthcare
What is Computer Vision?
Computer vision is a subset of artificial intelligence that enables machines to interpret and analyze visual data. In healthcare, computer vision is used to:
- Detect abnormalities in medical images such as X-rays, MRIs, and CT scans.
- Assist radiologists and doctors in diagnosing diseases with higher accuracy.
- Reduce human error and enhance patient outcomes through automated analysis.
The Rise of AI in Medical Imaging
Traditionally, medical imaging relied on the expertise of radiologists and pathologists who manually interpreted images. However, with the vast amount of data generated in modern healthcare, AI-driven computer vision has become essential. Some key milestones include:
- The introduction of deep learning algorithms in 2012, which significantly improved image recognition.
- The FDA’s approval of AI-powered diagnostic tools for detecting diseases like diabetic retinopathy.
- The integration of AI-driven imaging tools in hospitals and research facilities worldwide.
Applications of AI-Powered Computer Vision in Medical Diagnostics

Radiology and Imaging Analysis
One of the most significant applications of AI in healthcare is in radiology. AI algorithms can analyze medical images such as:
- X-rays: AI models detect fractures, infections, and lung diseases such as pneumonia.
- MRI and CT scans: AI assists in identifying tumors, stroke-related abnormalities, and neurodegenerative conditions.
- Ultrasound imaging: AI-powered systems improve prenatal screening and cardiovascular disease detection.
Pathology and Cancer Detection
Computer vision is transforming pathology by enabling faster and more accurate detection of cancerous cells. AI models can:
- Analyze biopsy slides to detect cancerous tissues.
- Differentiate between benign and malignant tumors.
- Assist pathologists in diagnosing diseases such as breast and prostate cancer with high precision.
Ophthalmology: Diagnosing Eye Diseases
AI is playing a crucial role in ophthalmology by analyzing retinal images to diagnose conditions such as:
- Diabetic Retinopathy: AI detects early signs of diabetic eye disease.
- Glaucoma: AI-assisted tools measure intraocular pressure and assess optic nerve damage.
- Age-Related Macular Degeneration (AMD): AI models help detect early-stage macular degeneration.
Dermatology: Skin Cancer and Disease Detection
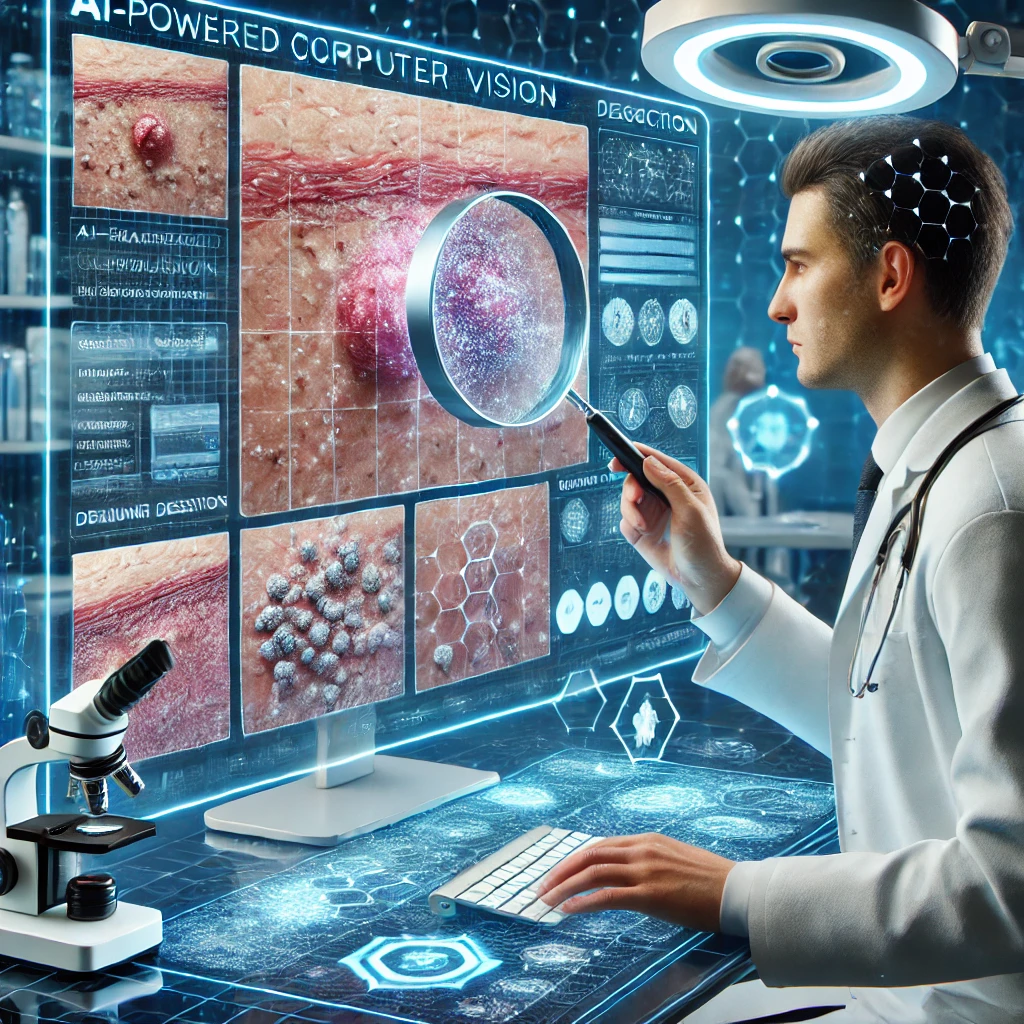

Computer vision is also making strides in dermatology. AI can:
- Identify malignant melanoma and other skin cancers.
- Detect skin conditions such as psoriasis, eczema, and fungal infections.
- Provide telemedicine support by allowing patients to scan their skin lesions and receive AI-based assessments remotely.
Advantages of AI in Medical Imaging
Improved Accuracy and Efficiency
AI-powered diagnostic tools reduce human error and improve accuracy in detecting diseases at an early stage. These tools analyze millions of medical images to recognize patterns that might be missed by human doctors.
Faster Diagnosis and Decision-Making
AI algorithms can analyze medical images in seconds, allowing doctors to make quicker and more informed decisions. This is especially crucial in emergency situations such as stroke or heart attack detection.
Cost Reduction in Healthcare
By automating the diagnostic process, AI reduces the need for multiple expensive tests and minimizes unnecessary medical procedures.
Enhancing Accessibility and Telemedicine
AI-driven diagnostic tools enable remote diagnosis, making healthcare more accessible to patients in rural or underserved areas.
Challenges and Ethical Considerations
Data Privacy and Security
Medical images contain sensitive patient data, and ensuring privacy and compliance with regulations like HIPAA and GDPR is crucial.
Bias in AI Models
AI models can sometimes inherit biases from the data they are trained on, potentially leading to disparities in healthcare outcomes.
Integration with Existing Healthcare Systems
Adopting AI in healthcare requires seamless integration with existing hospital infrastructure, which can be challenging and costly.
The Role of Human Expertise
While AI can assist in diagnostics, human doctors are still essential for interpreting results and making final treatment decisions.
Conclusion and What’s Next
AI-powered computer vision is revolutionizing healthcare diagnosis, making it more accurate, efficient, and accessible. As AI continues to advance, we can expect further improvements in real-time disease detection, personalized treatment plans, and AI-driven robotic surgery. However, challenges related to ethics, data security, and model bias must be addressed to ensure the responsible and equitable deployment of AI in medicine.
The next section will explore cutting-edge developments in AI-powered medical diagnosis, real-world case studies, and the future of AI-driven healthcare innovations.